Metre Bridge - Special Case of Wheatstone Bridge
Metre Bridge - Special Case of Wheatstone Bridge: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Meter Bridge, Sensitivity of Meter Bridge Experiment, Construction of Meter Bridge, Limitation of Meter Bridge & Kelvin's Method to Determine Resistance of Galvanometer etc.
Important Questions on Metre Bridge - Special Case of Wheatstone Bridge
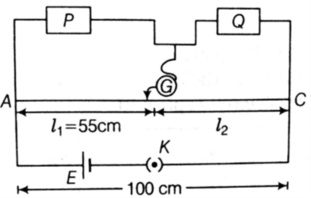
In a meter bridge balance point is found at a distance with resistances R and S as shown in the figure.
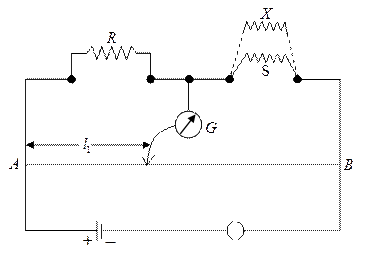
When an unknown resistance X is connected in parallel with the resistance S, the balance point shifts to a distance . Find the expression for X in terms of , and S.
In a meter bridge experiment, resistances are connected as shown in figure. The balancing length . Now, an unknown resistance is connected in series with and the new balancing length is found to be . The value of is (Given, )
How do you find the resistance of a wire using a meter bridge?
What is balance point in Kelvin's method of determination of galvanometer resistance Shaalaa?
What is the use of Kelvin's method?
What is the use of Kelvin's method?
What are the applications of meter bridge
Why meter bridge is not suitable?
What is meter bridge?
What are the limitation of Metre bridge?
On interchanging the resistances, the balance point of a meter bridge shifts to the left by 10 cm. The resistance of their series combination is . How much was the resistance on the left slot before interchanging the resistances?
In a meter Bridge experiment resistance is connected in the right gap. When and are connected in the left gap separately the balance points are and respectively from the left end. Now if both are connected in series in the left gap with in the right gap the new balance point from the left end (in ) is , what is the value of ?
The circuit diagram given in the figure shows the experimental setup for the measurement of unknown resistance by using a meter bridge. The wire connected between the points has non-uniform resistance such that resistance per unit length varies directly as the distance from the point Null point is obtained with the jockey with and in the given position. On interchanging the positions and in the gaps the jockey has to be displaced through a distance from the previous position along the wire to establish the null point. If the ratio of find the value of (in ). Ignore any end corrections. [Take ]
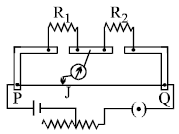
In the given meterbridge, is a wire of uniform cross-section and its resistivity changing from to as . If deflection in galvanometer is zero at such that , the value of is.
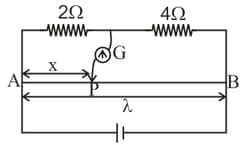
Figure shows a Meter bridge wire has uniform cross-section. The length of wire is is a standard resistor of and is a coil. When is immersed in melting ice the null point is at from point . When the coil is heated to a resistor has to beconnected in parallel with in order to keep the bridge balanced at the same point. The temperature coefficient of resistance of the coil is units. Find the value of .
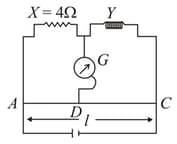
Consider the meter bridge circuit without neglecting end corrections. If we used and resistance in place of and respectively, we get null deflection at . If we interchange the resistances, the null deflection was found to be at . If and are the end correction, then the value of should be
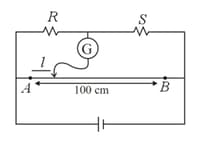
If the wire in the experiment to determine the resistivity of a material using metre bridge is replaced by copper or hollow wire the balance point i.e. null point shifts to
Null method is superior over deflection method because
Where do we get the balancing point of the meter bridge generally?
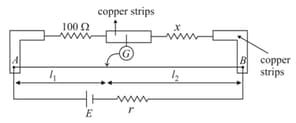
In a practical meter bridge circuit as shown, when one more resistance of is connected in parallel with unknown resistance , then ratio become . is balancing length. is a uniform wire. Then value of must be: